Page 246 - ISES SWC50
P. 246
German Technical Cooperation Agency GTZ
The following were projects listed in a case studies document prepared by the IEA-PVPS Task 9 – PV in
Developing Countries.
• In 1990 the German Government funded an “International Field-testing and Demonstration Programme
for Photovoltaic Water Pumps (PVP)”. The PVP programme was being conducted by the Deutsche
Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH (now GIZ). The GTZ implemented the PVP
Programme in co-operation with national energy and water authorities in Argentina, Brazil, Indonesia,
Jordan, the Philippines, Tunisia and Zimbabwe. In the course of the PVP Programme, a total of 90 PVP
systems had been installed at selected sites in the project countries. Those systems provided potable
water to people of the village communities and their livestock.
• In Nambia (1996) GTZ launched a pilot phase with approximately 100 SHS to provide the background
information for the design of a dissemination strategy. The findings from the pilot phase revealed that local
availability of skilled manpower, sound solar companies as system suppliers, as well as private ownership
of the SHS and avoidance of direct government subsidies are crucial success factors for the sustainable
dissemination of SHS in rural areas. The so-called Home Power! Program 4 was then launched in all 13
provinces of Namibia in 1997 and implemented in four annual phases up to 2001. Each phase was subject
to a public tender to select accredited suppliers.
World Bank Group
In the early 1990s, the World Bank Group (World Bank and International Finance Corporation IFC)) recognized
that solar home system technology was maturing, costs were declining, and commercial markets were
developing. At the same time, population growth was outpacing the ability of electric utilities to extend rural
electricity grids and developing countries were increasingly recognizing the economic difficulties of achieving
full grid-based rural electrification. The World Bank and many governments began to perceive that solar
home systems could provide least-cost rural electrification and could supplement grid-based electrification
policies. Between 1992 and 2000 the World Bank Group approved 10 projects. The following table provides
information on those approved during the 1990s.
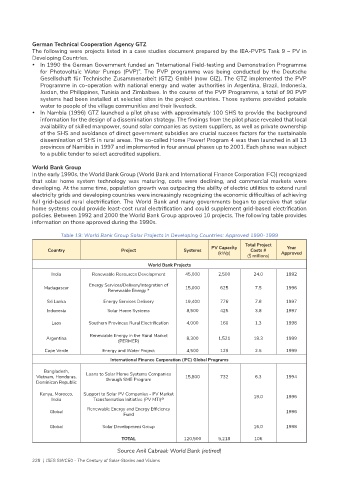
Table 19: World Bank Group Solar Projects in Developing Countries: Approved 1990-1999
Total Project
PV Capacity Year
Country Project Systems Costs #
(kWp) ($ millions) Approved
World Bank Projects
India Renewable Resources Development 45,000 2,500 24.0 1992
Energy Services/Delivery/Integration of
Madagascar 15,000 625 7.5 1996
Renewable Energy *
Sri Lanka Energy Services Delivery 19,400 776 7.8 1997
Indonesia Solar Home Systems 8,500 425 3.8 1997
Laos Southern Provinces Rural Electrification 4,000 160 1.3 1998
Argentina Renewable Energy in the Rural Market 8,300 1,521 18.3 1999
(PERMER)
Cape Verde Energy and Water Project 4,500 129 2.5 1999
International Finance Corporation (IFC) Global Programs
Bangladesh,
Vietnam, Honduras, Loans to Solar Home Systems Companies 15,800 732 6.3 1994
Dominican Republic through SME Program
Kenya, Morocco, Support to Solar PV Companies - PV Market 19.0 1996
India Transformation Initiative (PV MTI) @
Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency
Global Fund 1996
Global Solar Development Group 16.0 1998
TOTAL 120,500 5,218 106
Source Anil Cabraal: World Bank (retired)
228 | ISES SWC50 - The Century of Solar-Stories and Visions