Page 347 - ISES SWC50
P. 347
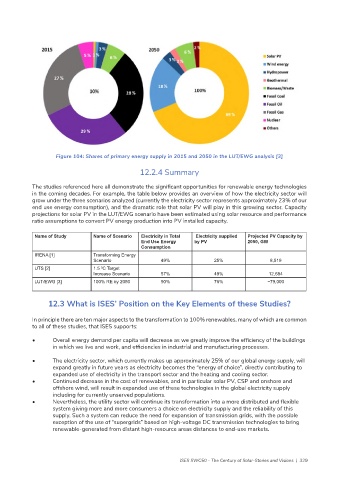
Figure 104: Shares of primary energy supply in 2015 and 2050 in the LUT/EWG analysis [3]
12.2.4 Summary
The studies referenced here all demonstrate the significant opportunities for renewable energy technologies
in the coming decades. For example, the table below provides an overview of how the electricity sector will
grow under the three scenarios analyzed (currently the electricity sector represents approximately 23% of our
end use energy consumption), and the dramatic role that solar PV will play in this growing sector. Capacity
projections for solar PV in the LUT/EWG scenario have been estimated using solar resource and performance
ratio assumptions to convert PV energy production into PV installed capacity.
Name of Study Name of Scenario Electricity in Total Electricity supplied Projected PV Capacity by
End Use Energy by PV 2050, GW
Consumption
IRENA [1] Transforming Energy
Scenario 49% 25% 8,519
UTS [2] 1.5 C Target
0
Increase Scenario 57% 49% 12,684
LUT/EWG [3] 100% RE by 2050 90% 76% ~79,000
12.3 What is ISES’ Position on the Key Elements of these Studies?
In principle there are ten major aspects to the transformation to 100% renewables, many of which are common
to all of these studies, that ISES supports:
• Overall energy demand per capita will decrease as we greatly improve the efficiency of the buildings
in which we live and work, and efficiencies in industrial and manufacturing processes.
• The electricity sector, which currently makes up approximately 25% of our global energy supply, will
expand greatly in future years as electricity becomes the “energy of choice”, directly contributing to
expanded use of electricity in the transport sector and the heating and cooling sector.
• Continued decrease in the cost of renewables, and in particular solar PV, CSP and onshore and
offshore wind, will result in expanded use of these technologies in the global electricity supply
including for currently unserved populations.
• Nevertheless, the utility sector will continue its transformation into a more distributed and flexible
system giving more and more consumers a choice on electricity supply and the reliability of this
supply. Such a system can reduce the need for expansion of transmission grids, with the possible
exception of the use of “supergrids” based on high-voltage DC transmission technologies to bring
renewable-generated from distant high-resource areas distances to end-use markets.
ISES SWC50 - The Century of Solar-Stories and Visions | 329